When we talk about 3D printing materials plastics like PLA(polylactic acid), ABS (acrylonitrile butadiene styrene) pop up in our heads, but the one thing which is the same is that they are rigid. Fortunately, we have “flexible filament”, as the name suggests that it is malleable or not rigid i.e., can be bent into any form. These flexible 3D printing filaments are the ones that are widely useful materials to have on the go.
What are the best flexible filament settings for 3D printers? The best flexible filament settings are decreased print speed, print layer distance, disable retraction, increase printing temperature, etc. There are several other flexible filament settings that can be used for better printing results. Some important of them are given in the post further.
Generally, the most commonly used material for commercial usage in numerous industries is NYLON. Due to their easily blend-able properties, they are mixed with other materials to form composites, enhancing their performance parameters and used in all manufacturing operations. But unfortunately, one major disadvantage for nylon it is prone to warping and is not easily bendable. Here comes our flexible filament in use.
In The Post:-
- Introduction & Common Problems
- Settings To Look For
- Flexible Filament Setting Steps
- Flexible Filament Types in Short
- FAQ’s on Flexible Filament
- Conclusion
Flexible Filament Short Introduction & Common Problems
These flexible 3D printing filaments are the ones that are widely useful materials to have at ready. Flexible filaments are easily printable rubber allowing you to create complicated and cumbersome elastic designs for any project and product based on the requirement. As the name signifies, “flexible” the key thing which makes it different from the other is that they are re-shapable. Mostly rubbers are thermosets through a process called “vulcanization” i.e., you heat it – shape it – cool it, and the shape is final and once it is formed you cannot change the shape. In 3D printing, you need the material in a way that it can be re-melted and molded into the desired shape and size.
TYPES OF 3D FLEXIBLE FILAMENTS
Under flexible 3D printing comes
- Thermoplastic PolyUrethane (TPU),
- Co-Polyamide ThermoPlastic Elastomer (PCTPE) or soft PLA.
These flexible filament has different chemical compositions and thus comprises of different properties, like the shore, hardness.
With so many surpluses, unfortunately, there are a lot more complications that are related to the 3D-printing with flexible filaments. Like, in the usual machinery setup when it extrudes the filament oozes out of the hot end. It doesn’t matter which type of extruder you have this is a common problem in the case of flexible filaments.
Usually in the normal filament (rigid) when the filament emerges out from the hot end it does not deviate whereas when treating with flexible filament when the filament oozes from the hot end and deviate which leads to the jamming at the hot end.
To help you we have simple slicer and printer settings that you can use to get better flexible prints.
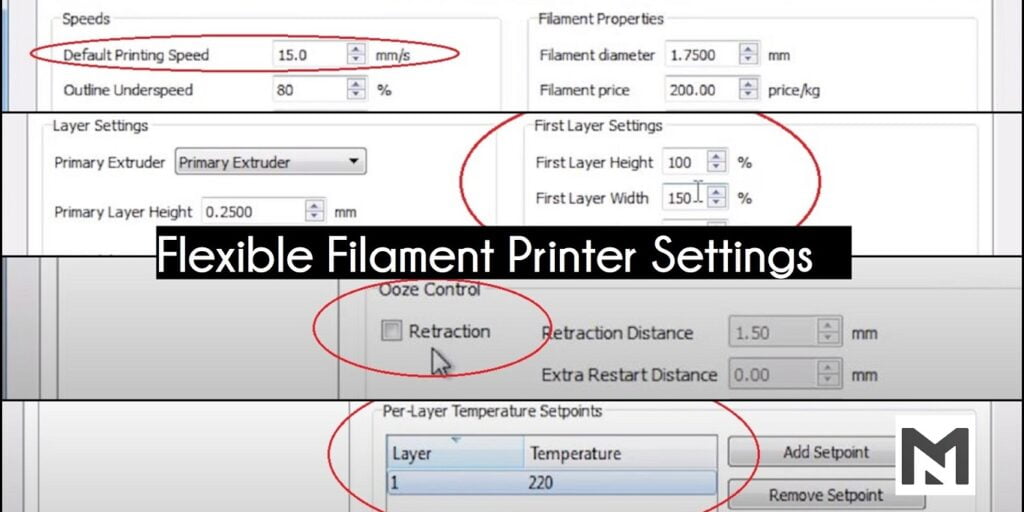
Settings For Flexible Filament To Look For
Increase Print Time: Slowing down the printing which leads to easy handling of the extruder through the hot end.
First Layer Settings: Maintain the appropriate distance between the surface and hot end for easy printing and thereby prevent jamming.
Disable Retraction: Retraction should not be carried as the consecutive contract and expansion make the flexible filament jam the nozzle at the hot end disabling allows the easy expulsion through the hot end.
Extrusion Multiplier: Increase the multilayer protrusion which helps the perimeter and layer to form bonds with each other properly. Under protrusion does not lead the perimeter and layers to form a strong bond with each other.
Printing Temperature: Depending upon the printing filament, increase the print temperature
Outlining: Avoid cross outlining, which makes the smooth out-coming of 3D printing and also decreases the time.
These are the simple settings that we can set to get even better flexible filaments 3D prints. Each of these flexible filament settings is discussed in detail below one by one to help you to eliminate the problems.
Flexible Filament Setting Steps
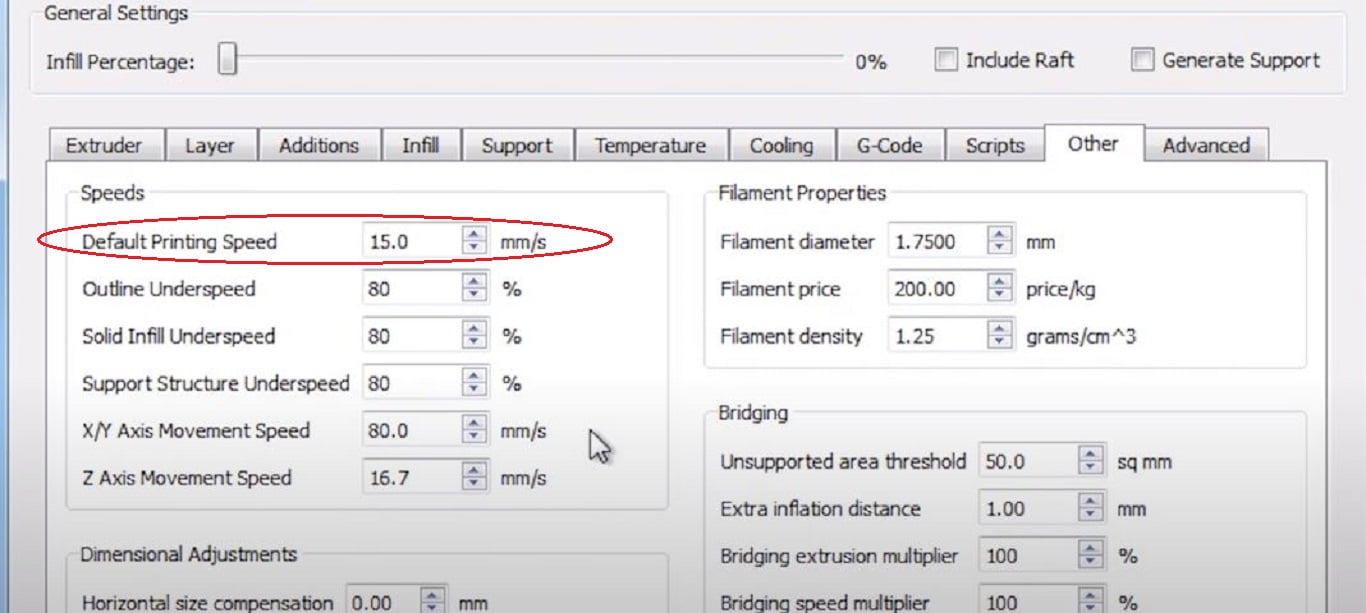
Print Speed
Flexible filaments are prone to compression and elongation thus we can’t print our flexible filaments at the speed of normal filaments.
- Under Printer setting in Other Settings Tab.
- Lower the default printing speed to half of the printing speed or as low as 15-16mm/s.
Print Layer Distance
Although it doesn’t is of major concern but sometimes it is too close and drags with the layer. So we have to be extra sure in the case of flexible filaments.
- Under the Printer setting in Layer Settings Tab.
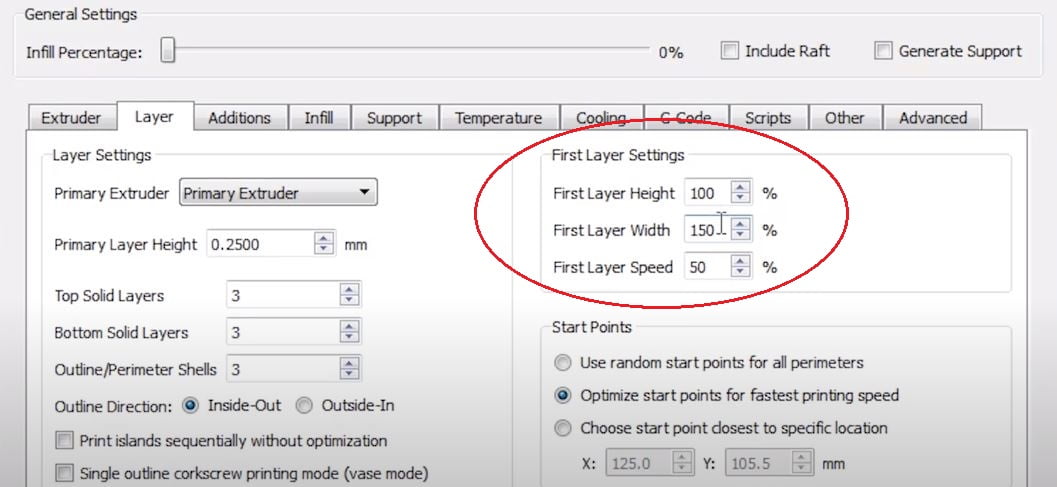
- Go to First Layer Settings section.
- First layer height (100%).
- First layer width(150%).
- First layer speed (50 to 60).
Disable Retraction Steps
Generally, with normal filaments, it is a super useful feature of extruders but with flexible filaments, it is a bad move. For flexible filaments when you keep retraction on the filaments is pushed forward and backward simultaneously and this makes it much more prone to jamming.
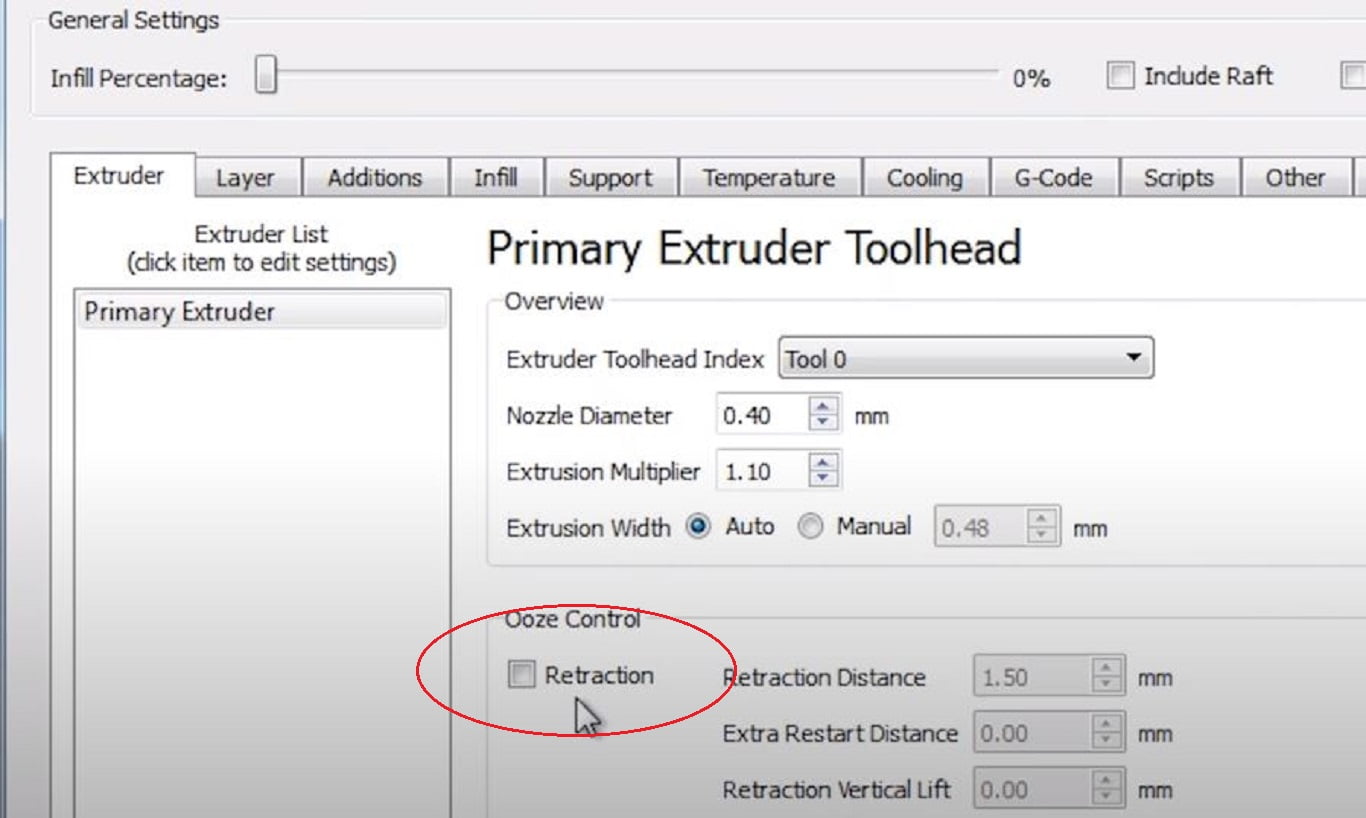
- Under printer setting in extruder tab.
- Go to the ooze control section
- Disable retraction by unchecking the retraction box.
Extrusion Multiplier
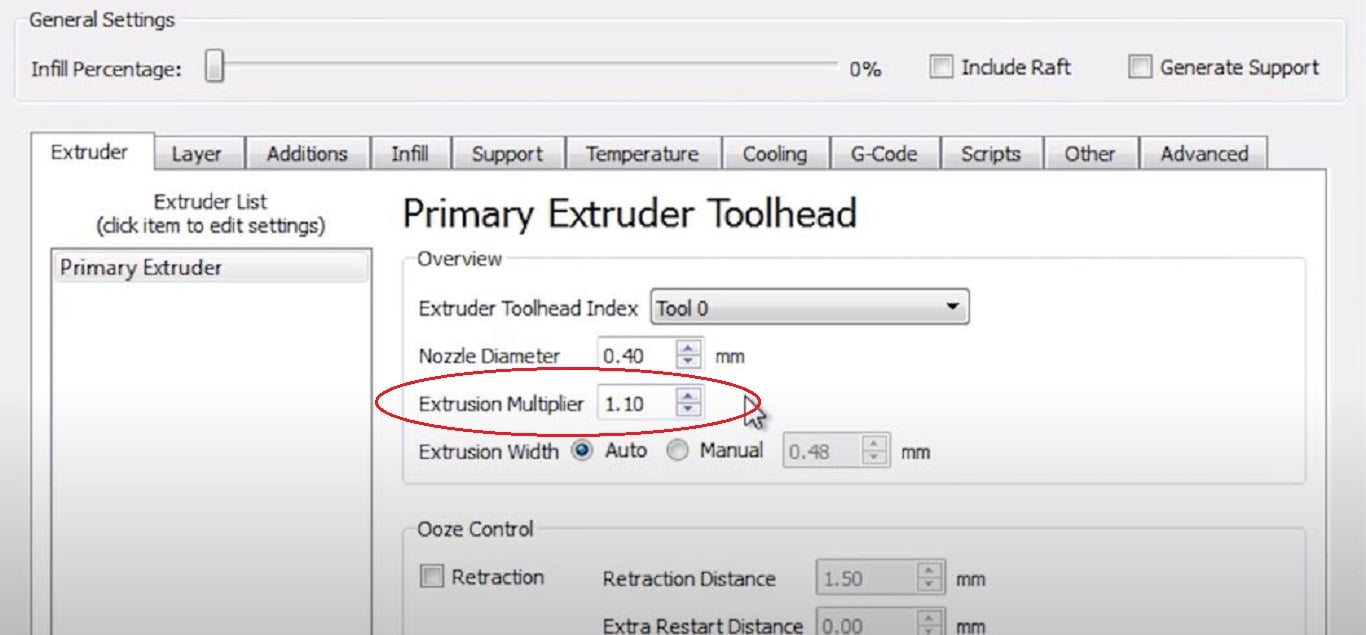
- Under printer settings in Extruder Tab.
- In the overview section set extrusion multiplier.
- Extrusion multiplier to 1.1 or less or equal (but greater than 1), so that perimeter and layers can bond together. You can check it for multiple values and decide for your filament on your own.
Disable Raft & Support
Supports in flexible filaments are not easily removable and thus we should avoid using them as much as possible.
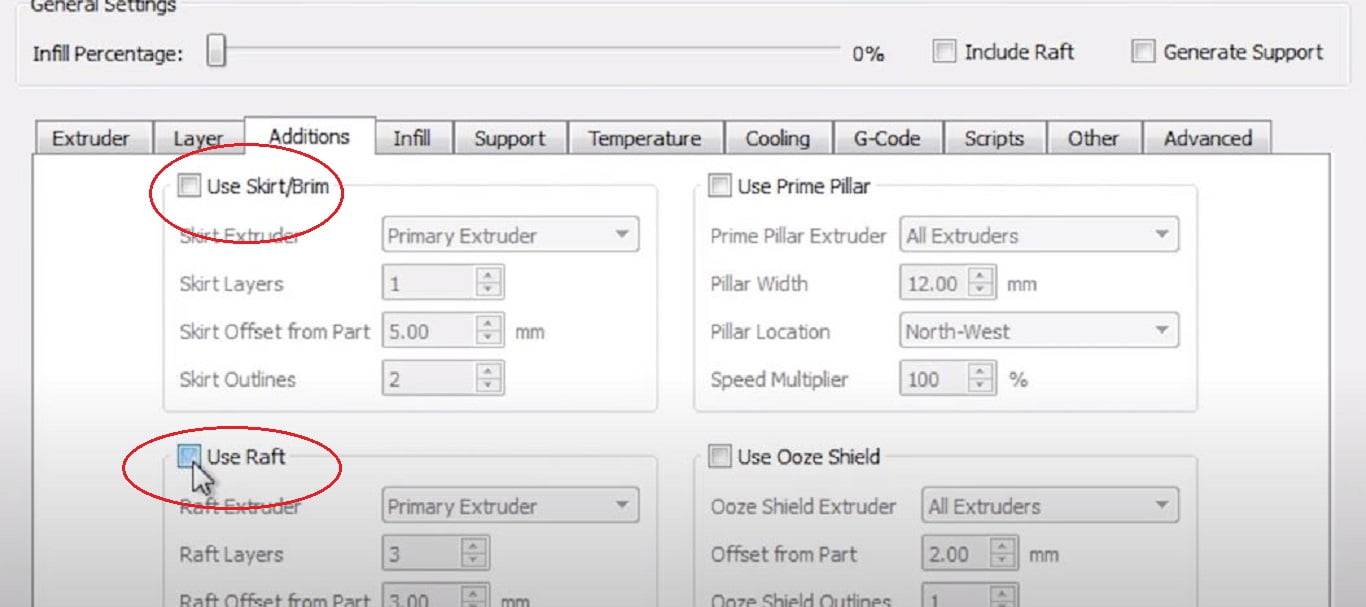
- Under printer settings in Additions Tab.
- Disable use raft by unchecking the option.
Enable Skirt
This makes your printer ready for the first layer by creating a skirting before going for the first layer.
- Under Additions Tab.
- Check the Skirt/Brim option to use this feature.
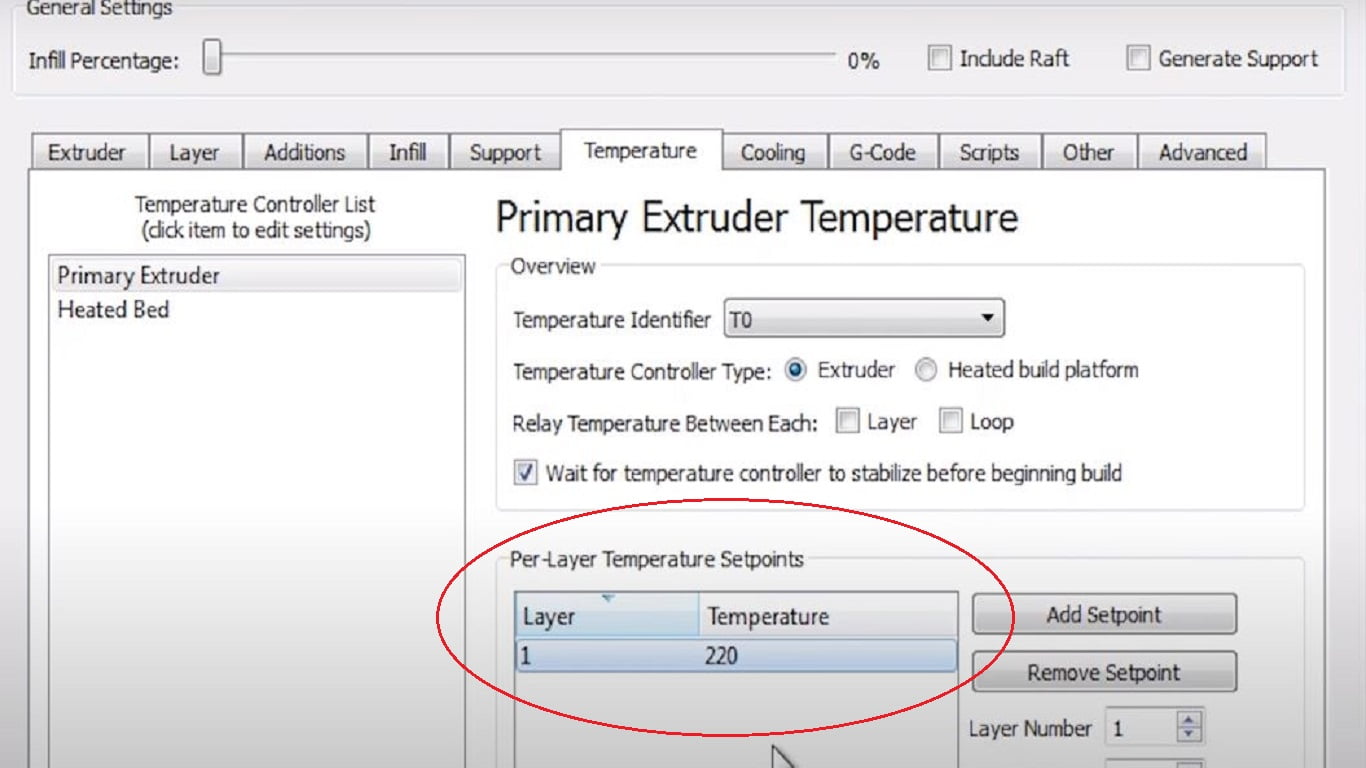
Increase Printing Temperature
This point is completely optional as it depends mainly on the types of filaments one is using. So you personally have to test different temperatures and compare them for the perfect temperature setting for your flexible filament.
- Under printer setting Temperature Tab.
- Select Primary extruder temperature.
- In Per layer temperature setpoints
- For our printer, we set the Temperature to 220-240֯ C.
Avoid Crossing Outline
During the crossing, extruders stop printing and move from one point to another, but sometimes during this process, a web-like thread is stretched especially in flexible filaments. To avoid this
- In Printer Settings go under Advanced Tab.
- Under Movement Behavior.
- Check avoid crossing outline for travel movements.
- You can also set the maximum allowed detour factor between 10-15.
Save The File
After doing everything kindly save all the settings so that one does need not to do all the settings again.
Flexible Filament Types in Short
Under flexible 3D printing flexible filaments is of mainly two types.
- Thermoplastic PolyUrethane (TPU),
- Co-Polyamide ThermoPlastic Elastomer (PCTPE) or soft PLA.
These flexible filament has different chemical compositions and thus comprises of different properties, like the shore, hardness.
Thermoplastic PolyUrethane (TPU)
Flexible filaments come up in ‘n’ numbers of color and chemical blend variations and hardness makes it usable for ‘n’ number of ways and one such class is TPU that have important properties such as elasticity, transparency, and resistance to the grease oil and also to abrasion.TPU provides excellent printability for 3d printing.
It is unique due to its extremely flexible nature. Technically in 3D printing technology usually polyacrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) and polylactic acid(LPA) are considered as standard plastic for printer filament but due to their insufficient flexibility, they cannot be used in bending prototypes. On the other hand, TPU printing filament is very flexible in nature. It can be bent easily without any effect on the design, strength, and durability.
Co-Polyamide ThermoPlastic Elastomer (PCTPE) or soft PLA
It has a chemical composition that makes it usable for high flexibility. It has low-temperature printability.PLA has the amalgamation of both nylon and rubber which provides them smooth lustrous texture and also provides more flexibility. It is because of this amalgamation that maintains higher durability.
FAQ’s on Flexible Filament
There are many settings that one could set to have a perfect flexible print. But, a few of the major ones are Print Speed, Print Layer Distance, Disable Retraction, etc.
Retraction causes the back and forth motion of the filament inside the extruder. Although it is a good feature in the case of normal filaments for flexible filaments, this causes bending of the filament and may result in extruder oozing or jamming.
Conclusion
After setting these options for your flexible filament you will see much better results than before. For some of the settings you may need to do trial and error as they differ for each type of flexible filament, the settings that need so are mentioned in the respective section.
If you have any doubt please ask in the comments section below, we are waiting for you to share your experiences with us.