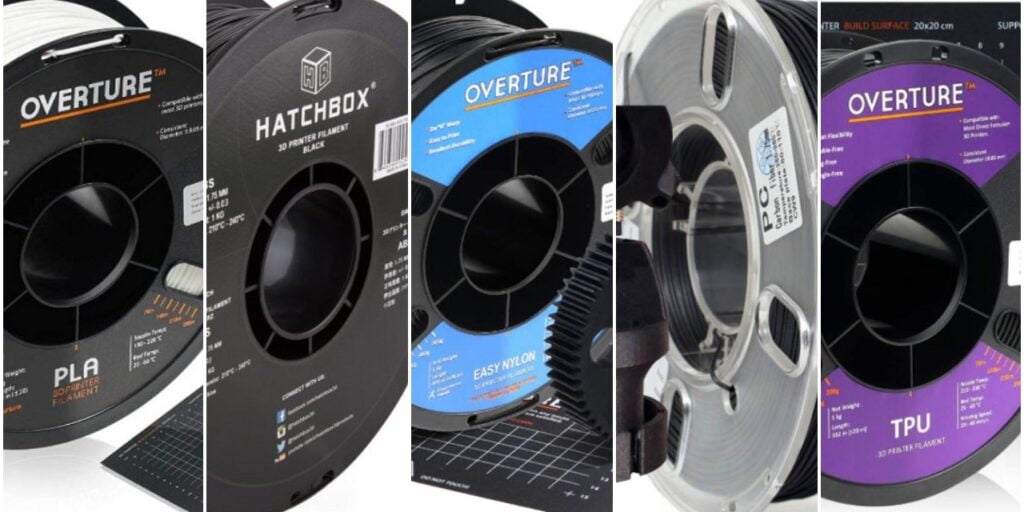
In today’s world 3d printing is easily available for prototyping, designing, small-scale manufacturing, and many more works. So wider use of 3d printing creates a variety of range of 3d printers Filament with different properties. If you search on the web for FDM printing filament types you will get a large list of filament types From which you have to choose the correct one for your print job which is not easy. For easy understanding, we give you a short note on each filament with its uses, major properties, and its pros and cons.
What are some common FDM printing filament types? The most common FDM technology filaments for general use are PETG, ABS, PLA, Nylon, PC, Flexible, and Glow in Dark filaments. All these are used by general 3d printer enthusiasts for simple prototyping and hobby printing. The major industrial use FDM filaments are Carbon Fibre, Metal, Glass Fibre, PVA, and Conductive filaments. All these filaments are discussed in this post along with some other major types.
As FDM printing is the safest and easiest 3D printing technology its consumer base is very large. Due to the large consumer base, there are many types of FDM printer filaments depending upon the use and properties. Here we have discussed the most important of the few.
In The Post:-
- FDM Printing Filaments Types: General Uses
- FDM Printing Filaments Types: Industrial Uses
- FAQ On Types of Filament
- Conclusion
FDM Printing Filaments Types For General Uses
PETG Filament
Its full form is Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol. It is mostly used for plastic bottles. PETG is a food-grade plastic due to its chemical-resistant properties. It has high strength and impact resistance. It is also used in the medical field for packaging and medical implants.
PETG is one of the best FDM printing filament types that consist of all properties which are good for any beginner person to use a good filament for their model.
PETG FIlament Uses
It can be used for multiple applications with different recommendations. But due to PETG filament’s properties, it is mostly used for moving parts or as a protective casing for them. Although we in our workspace mainly use it for prototyping purposes.
PETG Filament Properties
| Property | Values |
|---|---|
| Print Temperature | 220oC – 270oC |
| Heatbed Temperature | 60oC – 75oC |
| Food Grade | Yes (Note:- Not all PETG filaments are food grade) |
| Solubility | NO |
| Durability | High |
| Flexibility | Moderate |
| Easy of Use | Good |
| Fumes | Low Health Risk |
| Biodegradable | No |
Pros and Cons of PETG
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Stronger than PLA. | Considerable risks of wrapping. |
| Does not conduct electricity. | Absorb Moisture fast. |
| Chemical Resistance. | Less Biodegradable. |
The best PETG filament currently is Overture’s PETG Filament (Check Price on Amazon.com).

PLA Filament
PLA’s full form is PolyActide or Poly Acetic Acid. PLA is currently standard filament in 3d printing world. Every newbie of 3d printing starts with PLA because of its ease of use. In labs, it is known as polylactic Acid. It is easy to produced PLA so it is a cheap one also. It has biodegradable properties so it is also used in use and throw models.
PLA also reacts with acetone which makes its surface sticky so you can stick two PLA parts by applying acetone on their surface. This reaction with Acetone is also helpful in the post-processing of the model.
PLA Uses
Mostly PLA filament is used for teaching purposes because of its ease to use and low cost. PLA also use as a blend with other materials to form a multi-material filament.
PLA Filament Properties
| Property | Values |
|---|---|
| Print Temperature | 180oC – 220oC |
| Heatbed Temperature | 40oC – 60oC |
| Food Grade | No |
| Solubility | No |
| Durability | Medium |
| Flexibility | Moderate |
| Easy of Use | Very Good |
| Fumes | Low Health Risk |
| Biodegradable | Yes |
Pros and Cons of PLA
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Low Melting Point. | Not good for Mechanical Parts. |
| Biodegradable. | Sensitive to UV light. |
| Multiple options for the blend. | Some blend dissolves in Acetone. |
The best PLA Filament currently is Overture’s PLA Filament at a reasonable price. (Click here to check the price on Amazon.com)

ABS Filament
ABS filament’s full form is Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene. In FDM printing filament types ABS is well-known material. In our home, most plastic objects are made of ABS because of their mechanical and thermal properties. It is a rigid and high melting point which is considered good for use in hobby parts where you need strength flexibility and thermal property together.
ABS Uses
ABS is used for commercial prototyping because it is not easy to print with it you require high-temperature hot-end and you yourself also need to be a long-running player of 3d printing.
But with some precaution, you can also print with ABS at home for your use because When ABS is heated up to lower temperatures like 220oC it produced UFP (Ultra Fine Particle) which is a concern for the environment.
ABS Filament Properties
| Property | Values |
|---|---|
| Print Temperature | 200oC – 260oC |
| Heatbed Temperature | 70oC – 100oC |
| Food Grade | No |
| Solubility | No |
| Durability | High |
| Flexibility | Moderate |
| Easy of Use | Low (Require ALL Metal Hotend) |
| Fumes | Yes |
| Biodegradable | No |
| Abrasivity | Require Stainless Steel Nozzle or Cooper Nozzle |
Pros and Cons of ABS
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| High Durability. | Risk of Warping |
| Good for Mechanical Work. | Requires high-temperature parts. |
| Use acetone to make its surface sticky to glue on another sticky surface. | Sensitive to UV light. |
The best ABS Filament is Hatchbox ABS filament (Check Price on Amazon.com)

Nylon Filament
Nylon is a stiff, durable, flexible, and heat-resistant polymer. It also has low friction thus you use it in mechanical parts for low friction. It is extremely durable so if your project required low Friction, high strength, and good thermal properties then nylon is .best for you.
But it is not easy to print nylon it has a large risk of wrapping while printing. Nylon is an FDM printing filament type composite filament that also comes in different varieties.
Nylon Uses
Mechanical parts or for moving parts because of durability and flexibility. It is also UV resistant so you can use this for wearable object enclosers.
Nylon Filament Properties
| Property | Values |
|---|---|
| Print Temperature | 250oC – 270oC |
| Heatbed Temperature | 70oC – 100oC |
| Food Grade | No |
| Solubility | No |
| Durability | High |
| Flexibility | Good |
| Easy of Use | Low (Require All Metal Hotend) |
| Fumes | Yes |
| Biodegradable | No |
| Abrasivity | No |
Pros and Cons of Nylon Filament
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| High Strength | Requires all Metal Hotend |
| Flexible | Absorb Moisture easily |
| Impact Resistence | Expensive |
| Heat Resistance | Required Encloser and Experience for quality print |
The best Nylon FDM Filament with the best reviews is Overture’s Nylon Filament (Click Here to check the price on Amazon.com)

PolyCarbonate Filament (PC)
PolyCarbonate is high strength thermoplastic with optical clarity, it is also lightweight and flexible. For 3d printing with PolyCarbonate filament, you can not achieve 100% optical clarity but after print, you can use different treating processes to achieve 60 to 85% of optical clarity but with post-processing of the print, it looks icy cool and amazing.
PC Uses
PC is tough, optical clarity and heat resistance so it used in protective gearing equipment, CD & DVD and also it is a good insulator so you can use this for Encloser for electrical devices. It also deflects UV light so you can use this for protecting the shell from UV light.
PolyCarbonate Filament Properties
| Property | Values |
|---|---|
| Print Temperature | 270oC – 310oC |
| Heatbed Temperature | 90oC – 110oC |
| Food Grade | No |
| Solubility | No |
| Durability | High |
| Flexibility | Moderate |
| Easy of Use | Low (Require All Metal Hotend) |
| Fumes | Yes (Ventilation Required) |
| Biodegradable | No |
| Abrasivity | Yes (Requires Stainless Steel Nozzle) |
Pros and Cons
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| PC is incredibly tough and exile impact without any problem. | It is not easy to print with PolyCarbonate Filament. Higher risk of shrinking and warping. |
| Comes in different blend with other material. | Require all-metal hot-end and adhesive for heatbed. |
| After some post-processing steps, you can achieve 60 -80 % optical clarity. | Required Encloser for the printer if the surrounding temperature is not stable. |
Flexible Filament
Flexible filaments are blends of two or more materials depend on their properties. Usually, flexible filaments have multiple mixes so there are multiple flexible filaments in the market but the TPU version is mostly used.
TPE is a Thermoplastic Elastomer which is a combination of hard plastic and rubber while its Properties depend on their mix ratio. You need a direct drive extruder for flexible filament and slow print speed.
Flexible Filament Uses
Flexible filament mostly uses for making cases for objects which fit under the case. Some different blends have different properties like (low elasticity and high elasticity) thus it also uses to make tires for RC cars and grip sleeves. we also print vibration dampers with flexible filaments.
Properties of Flexible Filaments
| Properties | Value |
|---|---|
| Print Temperature | 225oC – 245oC |
| Heatbed Temperature | 45oC – 60oC |
| Food Grade | No |
| Solubility | No |
| Durability | Moderate |
| Flexibility | High |
| Easy of Use | Low (Require ALL Metal Hotend with Direct drive) |
| Fumes | Yes |
| Biodegradable | No |
| Abrasivity | No |
Pros and Cons of Flexible Filament
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Good Vibration Damping. | Absorb Moisture Easily. |
| Elastic and soft. | Hard to print with Bowden drive extruder(Required direct drive extruder). |
| Most of them are Chemical Resistant. | Print at low speed. |
The best Flexible Filament with the best reviews and our personal favorite is Overture’s TPU Flexible Filament (CHeck price on Amazon.com)

Glow In Dark Filament
Glow in the dark filament is not a single element filament but it’s a blend of light-absorbing material and other plastic. We can find glow dark filament version of most filament. Manufactures use strontium aluminate or Phporus zinc sulfate to blend with PLA, ABS, PETG, etc to create glow-in-dark filament. If you want to charge the glow in the dark filament fast you can use UV light which charges the filament fast.
Uses
Glow in dark filament use for a signboard that has to hang to be in a dark place. Often people use glow-in-dark filament with others object to give them a nice look in the dark.
Properties of Glow in Dark Filaments
| Properties | Value |
|---|---|
| Print Temperature | Different for different blends |
| Heatbed Temperature | Different for different blends |
| Food Grade | No |
| Solubility | No |
| Durability | Depend on blend |
| Flexibility | Depend on blend |
| Easy of Use | Medium |
| Fumes | Yes |
| Biodegradable | No |
| Abrasivity | Yes(Required Stainless Steel Nozzle) |
Pros and Cons of Glow in dark Filament
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Make Your model attractive. | Required Hardened nozzle. |
| Print custom holder for objects to easily find them in dark. | Required high infill for the high glow. |
| Available in different colors. | Print slow. |
FDM Printing Filaments Types for Industrial Uses
Carbon Fiber Filaments
Carbon Fibre Filament is a blend of carbon fiber and other plastics. PLA, PTEG, ABS, etc are also coming in carbon fiber versions which provide better stability of structural dimension with impact resistance and heat resistance also you got a nice shine surface finish.
Although whenever you start printing with a carbon fiber nozzle you need a hardened nozzle of steel or and other nozzles which is suitable for composite materials. Printing with carbon fiber filament has the risk of clogging so clean your nozzle before using it with a carbon fiber nozzle.
Uses
Carbon fiber mostly uses by hobbyists or by prototyping which has to suffer destructive testing. Carbon fiber also uses to print damaged tools parts because it is very stiff due to carbon particles but it also has brittleness so the stress amount applied to carbon fiber is limited.
Properties of Carbon Fiber Filaments
| Properties | Value |
|---|---|
| Print Temperature | Different for different blends |
| Heatbed Temperature | Different for different blends |
| Food Grade | No |
| Solubility | No |
| Durability | Depend on blend |
| Flexibility | Depend on blend |
| Easy of Use | Medium |
| Fumes | Yes |
| Biodegradable | No |
| Abrasivity | Yes (Required Stainless Steel Nozzle) |
Pros and Cons of Carbon Fiber Filaments
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| High strength and Stiffness | Require Hardened Nozzle. |
| Structural Stability | Clogging Risk. |
| Light Weight | Brittle in nature |
Priline’s Carbon Fiber is the best Carbon Fibre Filament for use. (Check price on Amazon.com)

Metal Filament
The metal filament is not made of pure metal but it is a mix of fine metal powder and binding agent which is any one of the plastics or polymer. After print successfully you need to do some post-processing cycle to get the pure metal parts. But it is not easy to print with metal powder if you print successfully but choose the wrong value for infill percentage then the part collapse or gives a bad surface finish.
Note:- After post-processing, your 3d print part is shrinking so take precautions while scaling the part.
Uses
Industrial prototyping and even small businesses use this technology for print with metal filament. Even curious people also use this filament for experiments but it also requires a temperature controllable furnace to burn the plastic and fuse the metal to form a complete metal part.
Today many online services are available for metal 3d printing you just need to send your cad to them and they print your part and do post-processing and send you metal part.
Properties of Metal Filaments
| Properties | Value |
|---|---|
| Print Temperature | Generally 190oC – 220oC |
| Heatbed Temperature | Different for different blends |
| Food Grade | No |
| Solubility | No |
| Durability | Depend on blend |
| Flexibility | No |
| Easy of Use | Medium |
| Fumes | Yes |
| Clogging Risk | Yes |
| Biodegradable | No |
| Abrasivity | Yes(Required Hardened Steel Nozzle or Ruby Nozzle) |
Pros and Cons of Metal Filament
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Metallic surface finish. | Required heavy-duty printer parts. |
| After the post-processing part is strong but brittle. | For post-processing furnace or oven is required. |
| Comes in Multiple Metal Options. | A hardened Nozzle is needed. |
Glass Fiber Filament
Glass fiber filament is the same as canon fiber filament but instead of carbon fiber manufacturers use glass fiber or for plastic in which it is mix used nylon. A combination of Nylon and Glass fiber makes a high impact resistance filament. Glass fiber printed parts are strong, Temperature resistant, and have high tensile strength. They don lose structural integrity when they got a high energy impact.
Uses
Glass fiber is best for mechanical parts because they have to exile a huge amount of force. Glass fiber is UV resistant and does not scratch easily so you can use this for the outer shell of the devices.
Properties of Glass Fibre Filament
| Properties | Value |
|---|---|
| Print Temperature | 250oC – 270oC |
| Heatbed Temperature | 60oC – 70oC |
| Food Grade | No |
| Solubility | No |
| Durability | High |
| Flexibility | Medium |
| Easy of Use | Low |
| Fumes | Yes |
| Clogging Risk | Yes |
| Biodegradable | No |
| Abrasivity | Yes(Requires Hardened Steel Nozzle) |
Pros and Cons of Glass Fibre Filament
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Good for Mechanical Work | Required all-metal hot-end |
| Rizid and Temprature Resistence | Printing is Slow |
| Maintain structural integrity while impact. | Risk of clogging |
PVA Filament
Poly Vinyl Alcohol filaments are water-soluble filaments. It is also the best FDM Printing Filament Types to use with Dual Extruder.
PVA filament is soluble in water so when you use a dual extruder system then use PVA as a support material after a print wash or just shink your model underwater for a while after this PVA dissolves in water only plastic model is left. Polyvinyl alcohol is very sensitive to moisture you need to put it in a dry box and also print from it directly. PVA is not completely biodegradable it requires some microorganisms to complete the degradation process.
Uses
PVA mostly uses for support and overhangs in 3d printing. In daily life, PVA mostly uses for making thin lining around soap and also use for fish bait.
Properties of PVA Filament
| Property | Values |
|---|---|
| Print Temperature | 190oC – 200oC |
| Heatbed Temperature | 45oC – 60oC |
| Food Grade | No |
| Solubility | Yes |
| Durability | Moderate |
| Flexibility | Medium |
| Ease of Use | High |
| Fumes | Yes |
| Biodegradable | Yes |
| Abrasivity | No |
Pros and Cons of PVA Filaments
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Using PVA as a support material makes your part surface fine. | 100% degradation of PVA requires microorganisms and enzymes. |
| PVA is Solubility in Water. | The handle of PVA is not easy because it breaks easily in presence of humidity or UV light. |
Conductive Filament
Conductive Filament is a new FDM printing filament type that is a mixer of carbon particles and normal plastic filament. It is best for use with a dual extrusion system because you `can make traces to conduct electricity in your model from which you can add electric stuff after the print is complete and did not require wiring. But there is also a limit you can use this filament only for low voltage applications.
Uses
Conductive filaments mostly use to make electrical paths in 3d models. Also, some people use this for teaching children how electronic circuit board design works. People also create capacitive switches with the filament for the game controllers or for something else that can e control by lo voltage signals.
Properties of Conductive Filament
| Property | Values |
|---|---|
| Print Temperature | 190oC – 200oC (Depend on filaments plastic type) |
| Heatbed Temperature | 45oC – 60oC (Depend on filaments plastic type) |
| Food Grade | No |
| Solubility | No |
| Durability | Moderate |
| Flexibility | Medium |
| Ease of Use | Medium (Required dual extruder for design and working) |
| Fumes | Yes |
| Biodegradable | No |
| Abrasivity | Yes |
Pros and cons of Conductive Filament
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Freedom to design PCB inside the plastic. | Required Dual Extruder for under-surface circuit design. |
| Some blends can handle more current. | It May catch fire if the circuit is overloaded. |
| Create customize electric parts. | Increase in resistance as the Path of the circuit increase. |
FAQ on Types of Filament
The 5 major types of FDM filaments for general use are PLA, PETG, ABS, Flexible, and Nylon filament.
The 3 major types of FDM filaments for industrial uses are Metal, Carbon Fibre, and PVA filaments.
PVA and PLA FDM filament is the most common bio-degradable filament in FDM 3d printing industry.
Conclusion
After all, we know that there are many more FDM printing filament types that are suitable for different types of jobs but when you are stuck to choose the correct one for your project then just think about which types of work project do and the types of environment it has to be used in.
We are waiting for your feedback on this post on FDM printing filament types. Also, share it with your friends. Thank You.